Definition
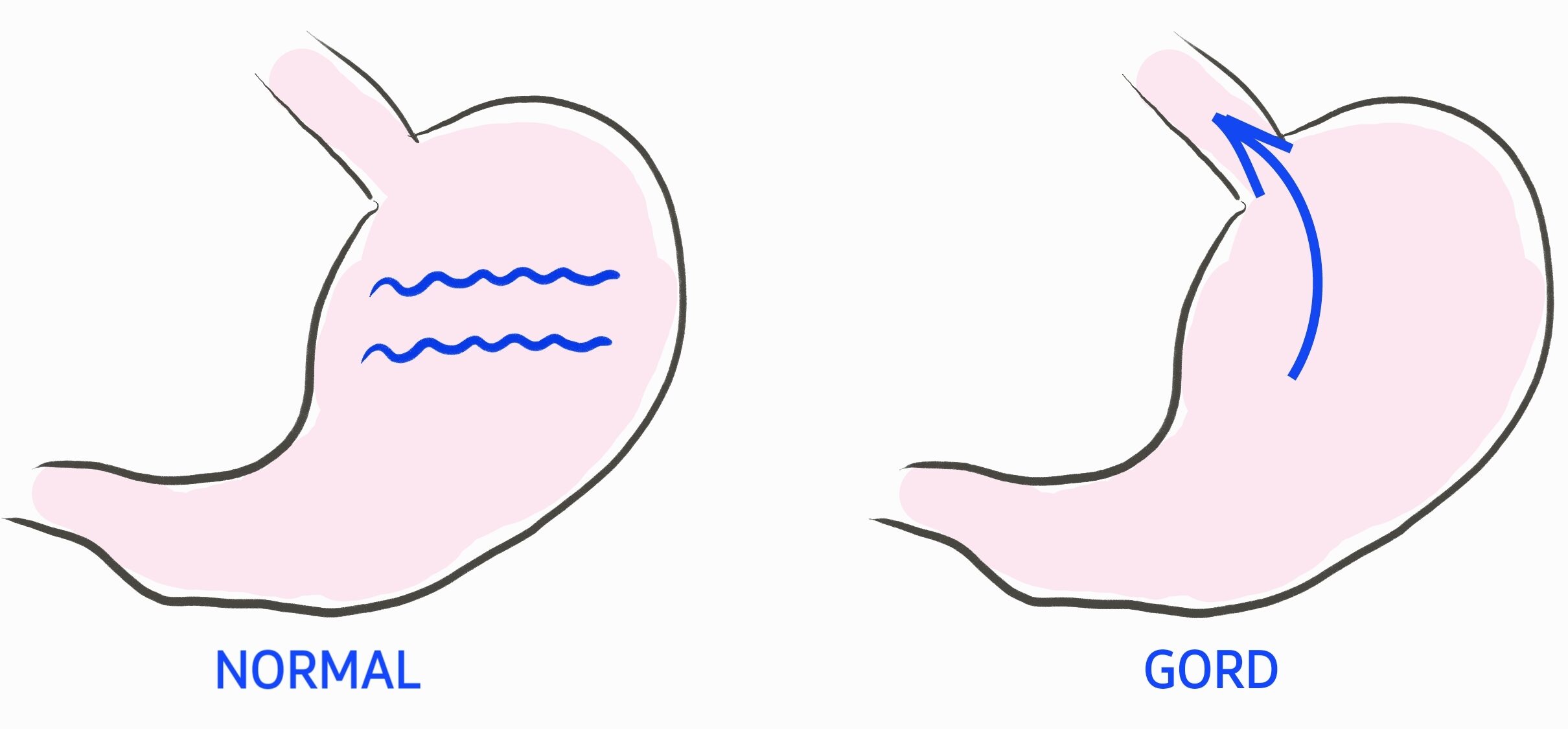
Gastro oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a common chronic condition where stomach contents including acid produced by the stomach leak into the oesophagus.
Etiology- Common causes:
- Increased relaxation of lower oesophagus sphincter
- Imbalance between intragastric and lower oesophageal sphincter pressure
- Impaired oesophageal acid clearance
- Hiatus hernia
- Risk factors:
- Smoking
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Psychological stress
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Gastrectomy
- Typical symptoms
- Retrosternal burning pain (Heartburn)
- Regurgitation
- Dysphagia
- Atypical symptoms
- Pressure sensation in the chest/noncardiac chest pain
- Belching, bloating
- Dyspepsia, epigastric pain
- Nausea
- Halitosis
- Extraoesophageal symptoms
- Chronic nonproductive cough and nighttime cough
- Hoarseness
- Dental erosions
- Aggravating factors
- Lying down shortly after meals
- Certain foods/drinks
- Atypical symptoms: consider an endoscopic evaluation if alarm features present:
- Dysphagia
- Odynophagia
- Early satiety
- Anaemia or evidence of GI bleeding
- Persisting vomiting
- Unintentional weight loss
- Aspiration pneumonia
- No improvement after PPI
- Oesophageal pH monitoring indicated if the following is present:
- Refractory GORD symptoms despite PPI therapy
- Evaluation before surgical or endoscopic antireflux procedure
- Consider other diagnoses such as peptic ulcer disease, CVD
- Lifestyle changes
- Dietary:
- Small portions, avoid eating 3 hours before bedtime, avoid triggering food and drinks
- Physical:
- Weight loss if obese, elevate head of the bed
- Reduce triggers
- Smoking, alcohol, caffeine, medication (eg. CCBs, diazepam)
- Dietary:
- Pharmacological Therapy
- PPIs for 8 weeks:
- Continue if good response
- Increase dose if partial response
- Stop if no response
- H2 receptor antagonist:
- Alternative GORD treatment
- Combined therapy with PPI for nighttime symptoms
- PPIs for 8 weeks:
 Surgical Therapy
Surgical Therapy
- If the previous two failed
- Fundoplication (creating artificial sphincter with gastric fundus)
